Free Vibration Analysis of Laminated Composite Plates Based on the Reconstructed Edge-Based Smoothing DSG Method
-
摘要:
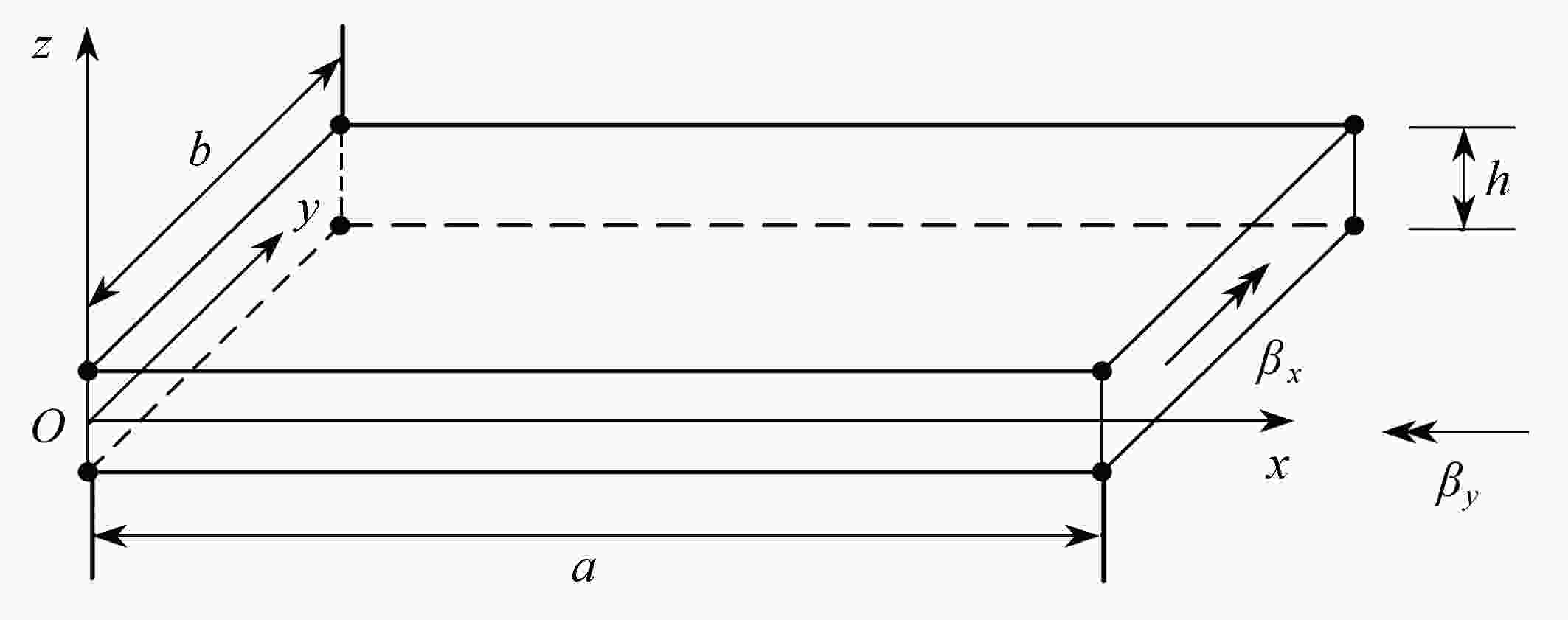
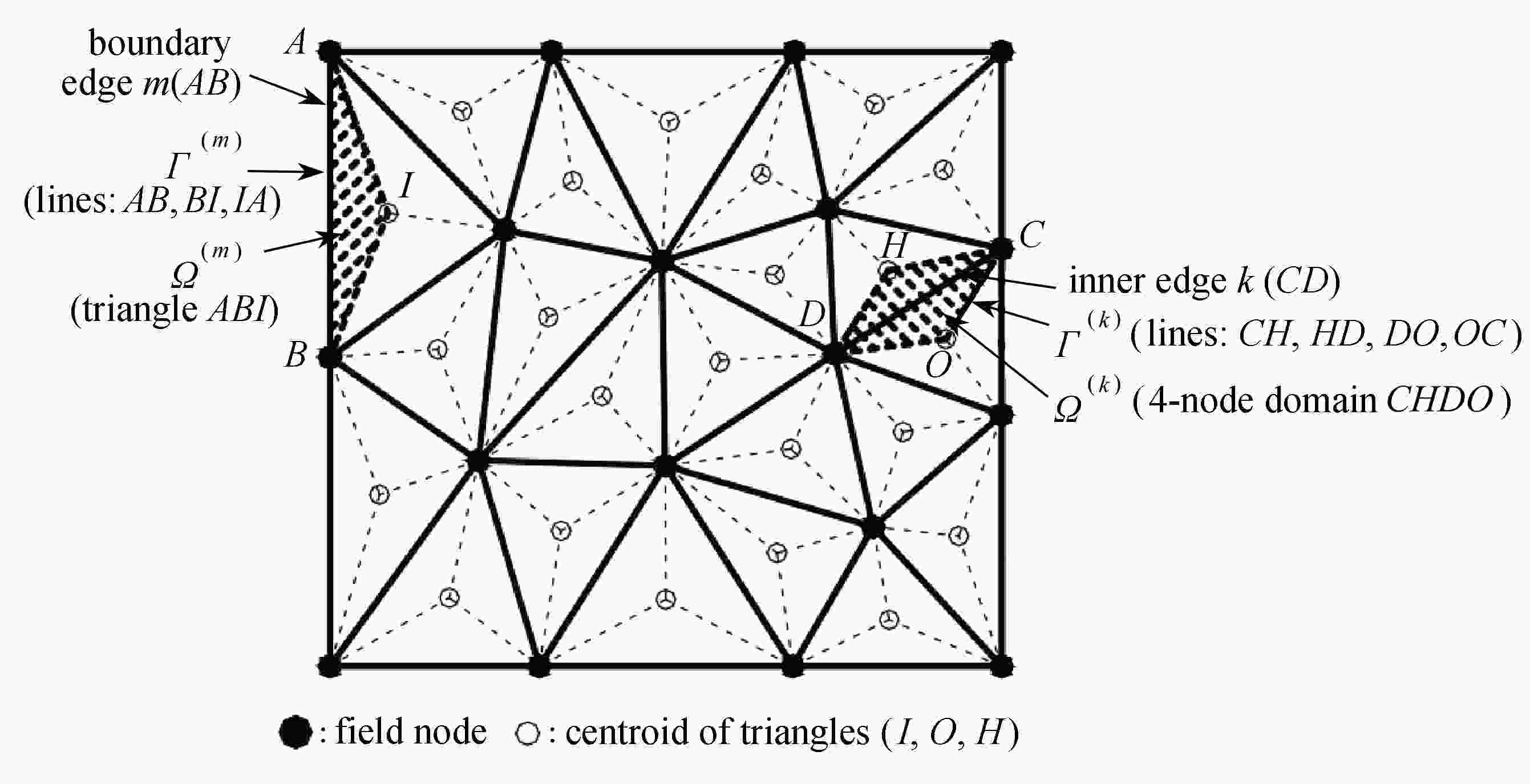
重构边界光滑离散剪切间隙(RES-DSG3)法,利用边界光滑技术将域积分转化为沿光滑域边界的边界积分,结合基于全局坐标系的非等参离散剪切间隙(DSG)法,避免了坐标映射和Jacobi矩阵的计算,同时克服了“剪切自锁”现象,提高了计算的精度。基于一阶剪切变形理论,采用该文给出的方法,从不同材料参数、边厚比、边界条件等几个方面对复合材料层合板自由振动固有频率进行了数值分析,通过典型算例的计算,验证了该方法的可行性和有效性。
Abstract:To avoid transverse shear locking and improve the accuracy, the RES-DSG3 method was proposed through the incorporation of the non-isoparametric DSG method with a novel edge-based smoothing technique based on global coordinates, and all the integration of smoothed matrices can be calculated along the boundary segments of smoothed cells without coordinate mapping. Based on the 1st-order shear theory, the RES-DSG3 method was used to analyze free vibration natural frequencies of laminated composite plates with different material parameters, edge-thickness ratios and boundary conditions. The free vibrations of the composite plates were analyzed numerically. The calculation of the example verifies the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 四层复合材料简支层合板的一阶无量纲固有频率
Table 1. The non-dimensional 1st fundamental frequency of the simply supported 4-layer laminated composite plate
表 2 三层复合材料层合板的一阶无量纲固有频率
Table 2. The non-dimensional 1st fundamental frequency of the 3-layer laminated composite plate
a/h method SS SC CC a/h method SS SC CC 2 ref. [22] 5.211 5.217 5.263 10 ref. [22] 14.804 17.199 19.678 ref.[21] 5.205 5.211 5.257 ref. [21] 14.767 17.175 19.669 present 5.149 5.571 5.256 present 14.475 17.346 19.626 5 ref. [22] 10.207 10.658 11.274 100 ref. [22] 18.355 28.165 40.234 ref. [21] 10.290 10.646 11.266 ref. [21] 18.891 28.501 40.743 present 10.116 10.675 11.477 present 18.565 28.616 40.761 表 3 三层复合材料层合板前三阶无量纲固有频率(a/h=10)
Table 3. The non-dimensional 1st 3 fundamental frequencies of the 3-layer laminated composite plate (a/h=10)
-
[1] 罗英勤, 李华东, 洪明. 复合材料层合板振动特性基础研究综述[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2020(1): 114-119LUO Yingqin, LI Huadong, HONG Ming. Review of the vibration characteristics of composite laminated plates[J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2020(1): 114-119.(in Chinese) [2] 叶天贵, 靳国永, 刘志刚. 基于改进Chebyshev级数的层合结构振动分析新理论[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(1): 58-74YE Tiangui, JIN Guoyong, LIU Zhigang. A new layerwise theory for vibration analysis of laminated structures based on modified Chebyshev polynomials[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 58-74.(in Chinese) [3] 刘旭, 姚林泉. 热环境中旋转功能梯度纳米环板的振动分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(11): 1224-1236LIU Xu, YAO Linquan. Vibration analysis of rotating functionally gradient nano annular plates in thermal environment[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(11): 1224-1236.(in Chinese) [4] 童瑶, 姚玉喆. 基于20节点辛元的复合材料层合板应力分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(5): 509-516TONG Yao, YAO Yuzhe. 20-node hexahedron symplectic elements for stress analysis of composite laminates[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(5): 509-516.(in Chinese) [5] CALIRI M F, FERREIRA A J, TITA V. A review on plate and shell theories for laminated and sandwich structures highlighting the finite element method[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 156(15): 63-77. [6] LIU G R, DAI K Y, NGUYEN T T. A smoothed finite element method for mechanics problems[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2007, 39(6): 859-877. doi: 10.1007/s00466-006-0075-4 [7] LIU G R, NEUYEN-THOI T, NGUYEN-XUAN H, et al. A node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) for upper bound solutions to solid mechanics problems[J]. Computers and Structures, 2009, 87(1/2): 14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2008.09.003 [8] LIU G R, NEUYEN-THOI T, LAM K Y. An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for static, free and forced vibration analyses of solids[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, 320(4/5): 1100-1130. [9] NEUYEN-THOI T, LIU G R, LAM K Y, et al. A face-based smoothed finite element method (FS-FEM) for 3D linear and geometrically non-linear solid mechanics problems using 4-node tetrahedral elements[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2009, 78(3): 324-353. doi: 10.1002/nme.2491 [10] LEE K, SON Y, IM S. Three-dimensional variable-node elements based upon CS-FEM for elastic-plastic analysis[J]. Computers and Structures, 2015, 158: 308-332. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.06.005 [11] 秦剑波, 谢伟, 王锋. 基于光滑边域有限元法的二维裂纹扩展分析[J]. 应用力学学报, 2019, 36(1): 47-52, 252QIN Jianbo, XIE Wei, WANG Feng. An analysis of 2D crack growth based on ES-FEM[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2019, 36(1): 47-52, 252.(in Chinese) [12] NEUYEN-THOI T, PHUNG-VAN P, NGUYEN-XUAN H, et al. A cell-based smoothed discrete shear gap method using triangular elements for static and free vibration analyses of Reissner-Mindlin plates[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2012, 91(7): 705-741. doi: 10.1002/nme.4289 [13] 游翔宇, 郑文成, 李威, 等. 基于边光滑有限元法的加筋板静力和自由振动分析[J]. 计算力学学报, 2018, 35(1): 28-34YOU Xiangyu, ZHENG Wencheng, LI Wei, et al. Static and free vibration analysis of stiffened plates by ES-FEM using triangular element[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2018, 35(1): 28-34.(in Chinese) [14] NATARAJAN S, FERREIRA A J, BORDAS S P A, et al. Analysis of composite plates by a unified formulation-cell based smoothed finite element method and field consistent elements[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 105: 75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.04.040 [15] 林晓珊, 杨晓翔, 高剑虹. 基于扩展有限单元法的短纤维/橡胶复合材料裂纹扩展分析[J]. 固体力学学报, 2022, 43(1): 81-94LIN Xiaoshan, YANG Xiaoxiang, GAO Jianhong. Crack propagation analysis of short fiber reinforced rubber composites based on extended finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2022, 43(1): 81-94.(in Chinese) [16] BLETZINGER K-U, BISCHOFF M, RAMM E. A unified approach for shear-locking-free triangular and rectangular shell finite elements[J]. Computers and Structures, 2000, 75(3): 321-334. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7949(99)00140-6 [17] NGUYEN-XUAN H, LIU G R, THAI-HOANG C, et al. An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner-Mindlin plates[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 199(9/12): 471-489. [18] NGUYEN-XUAN H, RABCZUK T, NGUYEN-THANH N, et al. A node-based smoothed finite element method with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner-Mindlin plates[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2010, 46(5): 679-701. doi: 10.1007/s00466-010-0509-x [19] YANG G, HU D A, LONG S Y. A reconstructed edge-based smoothed DSG element based on global coordinates for analysis of Reissner-Mindlin plates[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2017, 33: 83-105. doi: 10.1007/s10409-016-0607-x [20] LIU G R, DAI K Y, NGUYEN T T. A smoothed finite element method for mechanics problems[J]. Computational Mechanics. 2007, 39: 859-877. [21] REDDY J N. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells: Theory and Analysis[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1997. [22] FERREIRA A, ROQUE C, JORGE R. Free vibration analysis of symmetric laminated composite plates by FSDT and radial basis functions[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 194(39/41): 4265-4278. [23] KHDEIR A A, LIBRESCU L. Analysis of symmetric cross-ply laminated elastic plates using a higher-order theory part Ⅱ: bucking and free vibration[J]. Composite Structures, 1988, 9(4): 259-277. doi: 10.1016/0263-8223(88)90048-7 -




 下载:
下载:


 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号