Simulation of Aerodynamic Performances of Flexible Flapping Wing Airfoils
-
摘要:
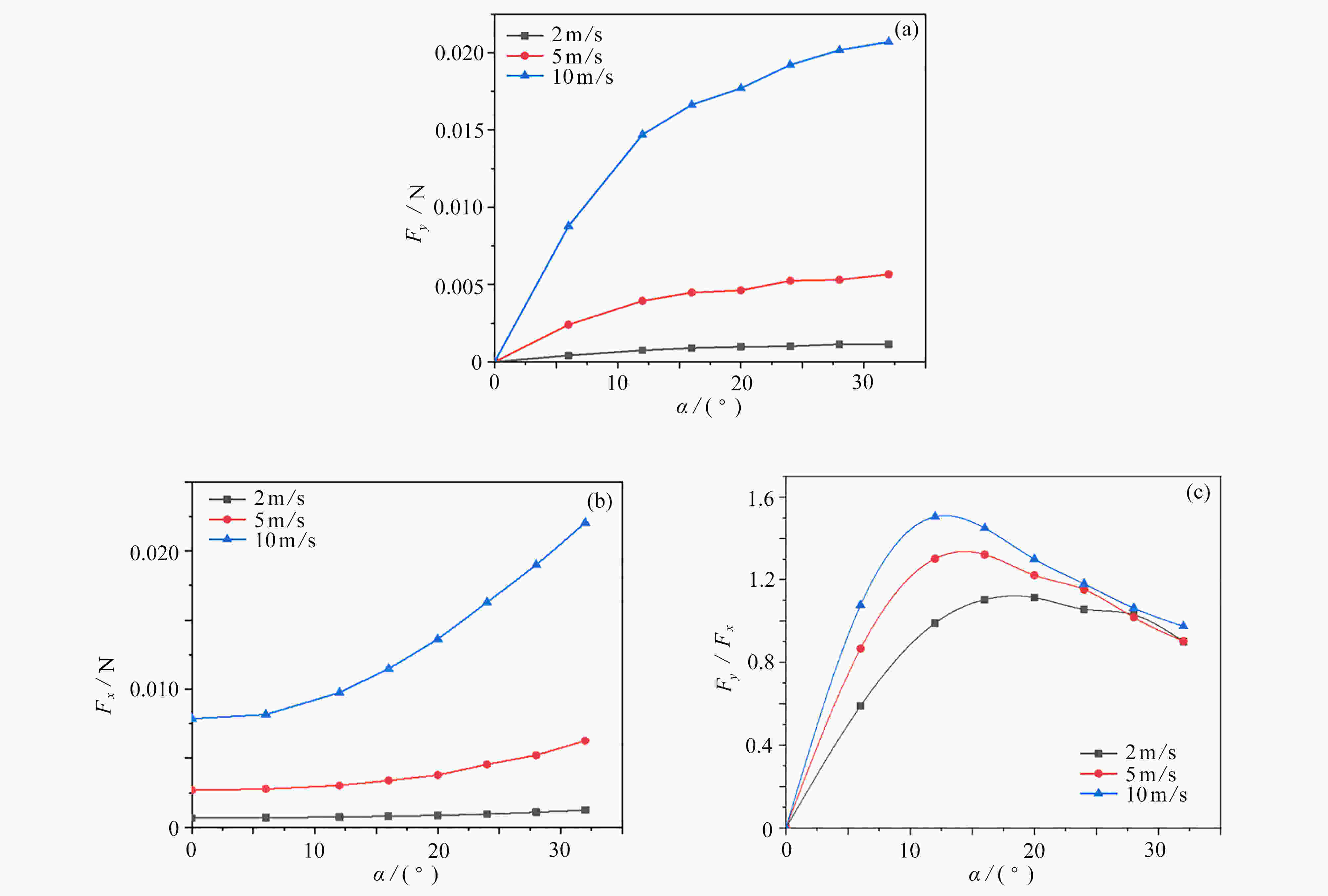
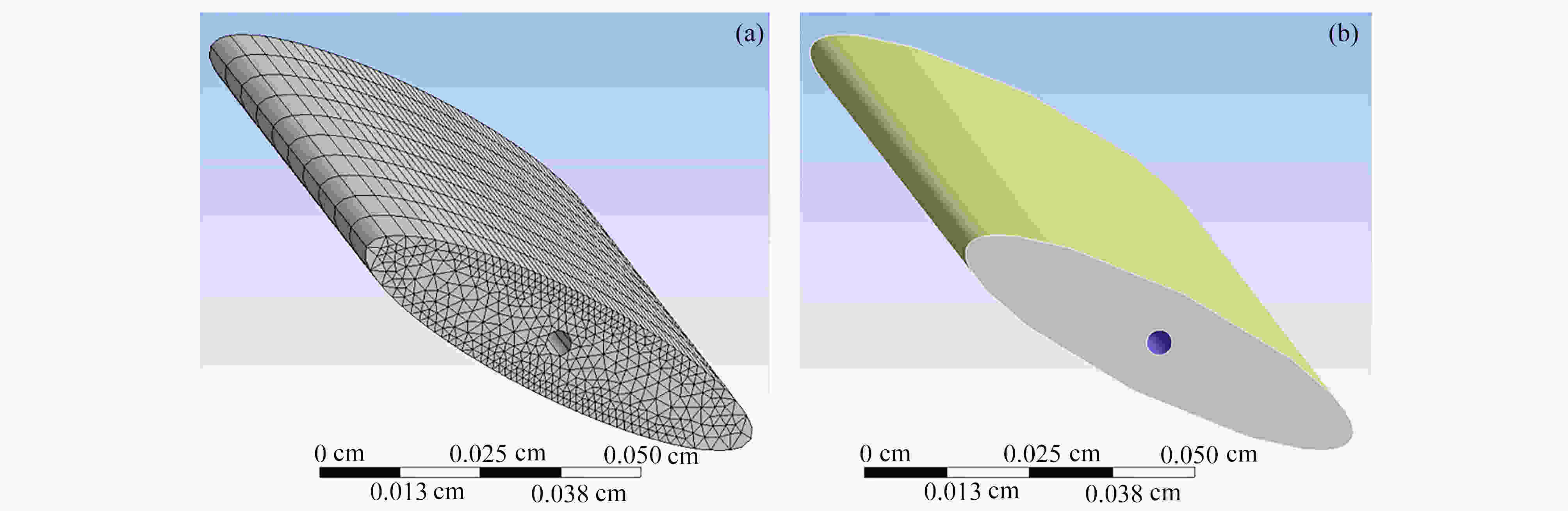
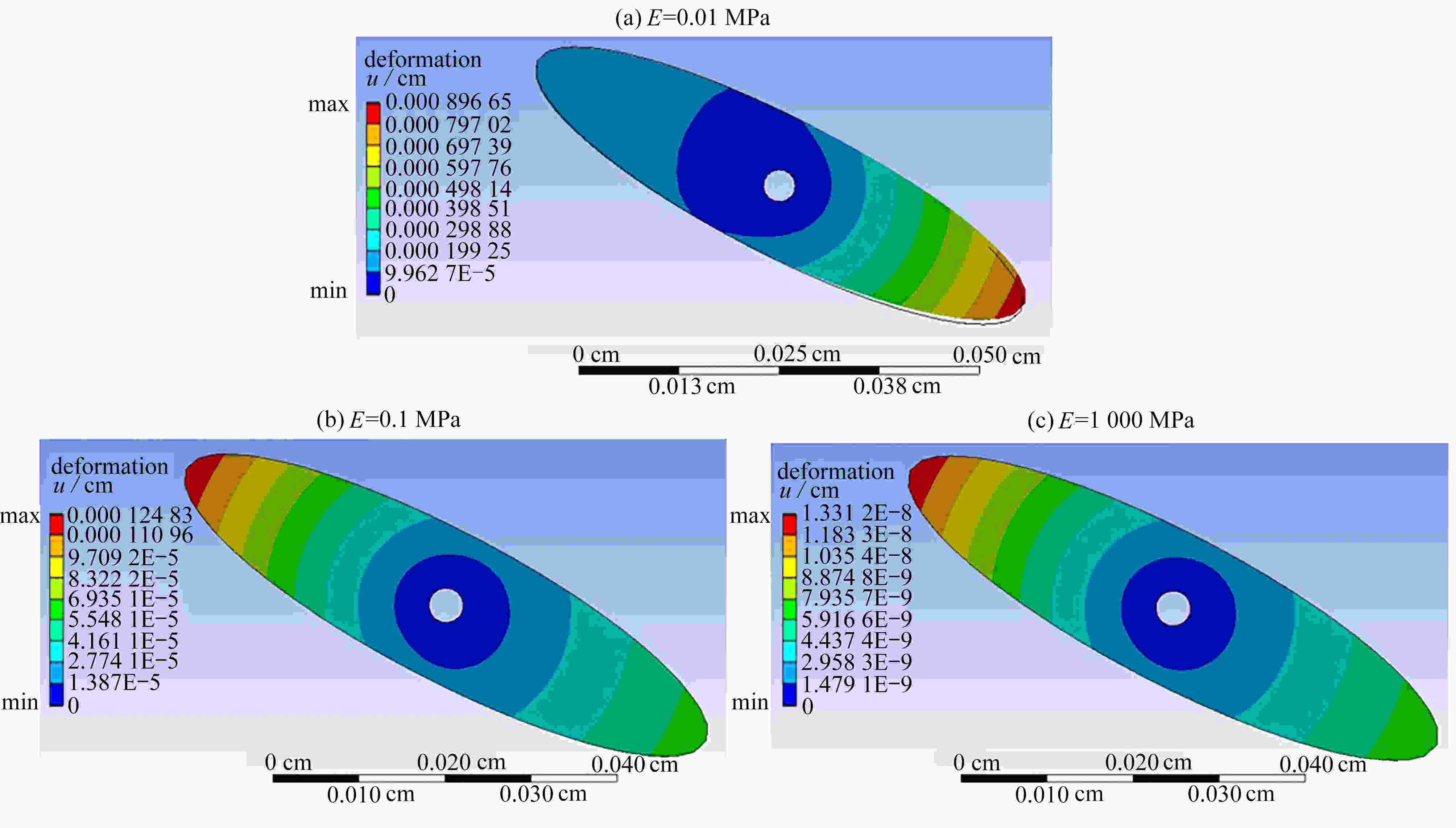
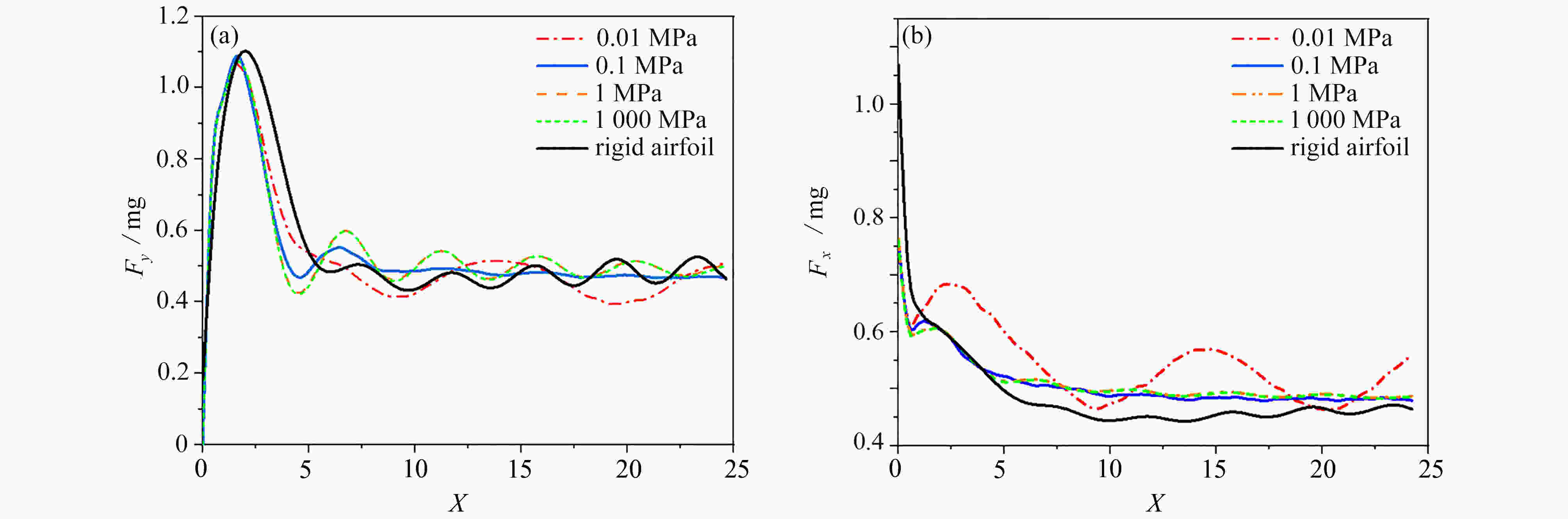
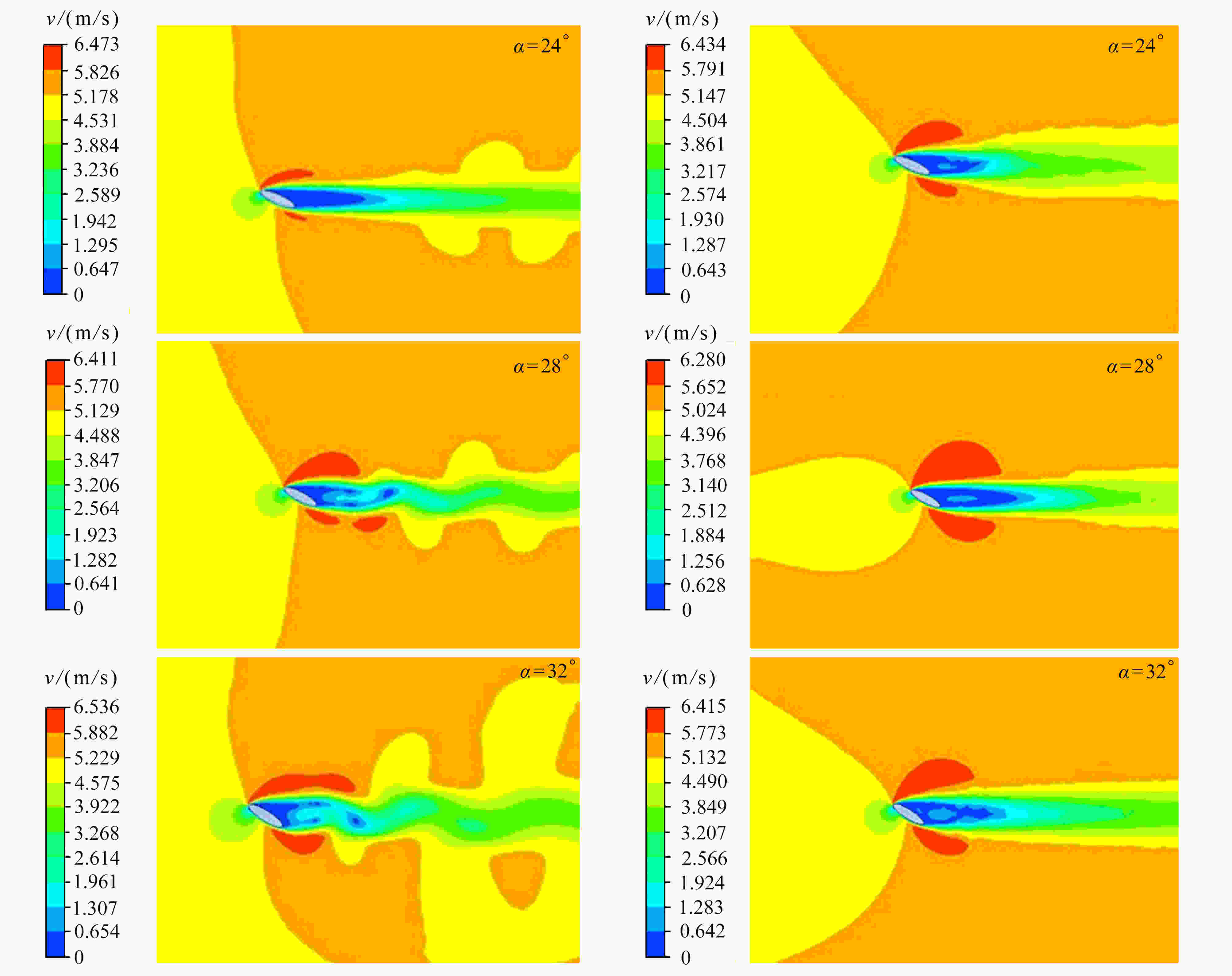
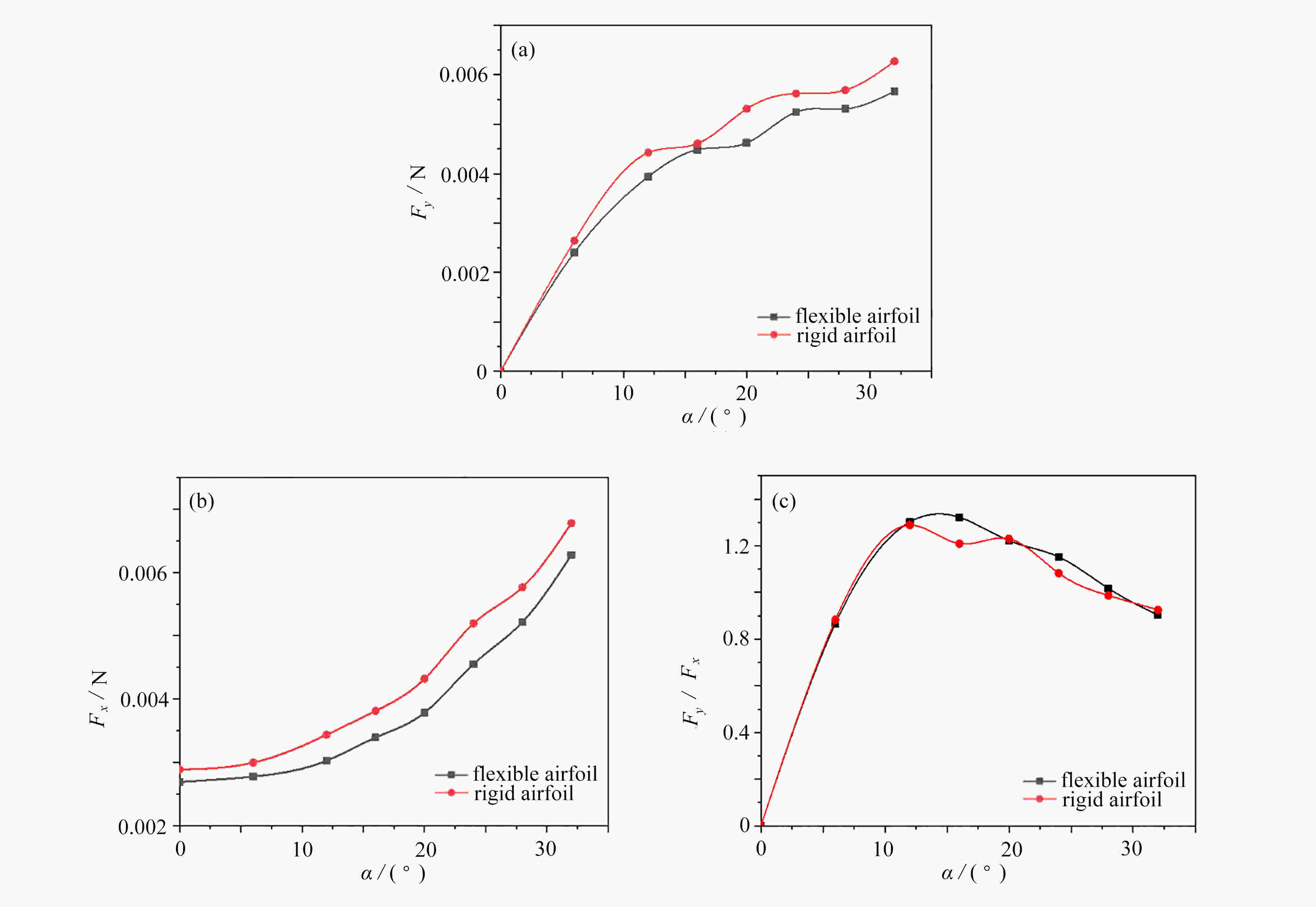
与固定翼相比,在低速、小Reynolds数条件下,扑翼飞行具有显著的气动性能优势,受到越来越多的重视。然而,目前对扑翼翼型的研究以刚性翼型为主,对柔性翼型气动性能认识还不清楚。该文建立了柔性椭圆翼型的流固耦合仿真模型,分析了不同风速、迎角下柔性椭圆翼型的周围流场、变形以及气动性能。仿真结果表明,较刚性翼型,柔性翼型延缓了尾涡脱落时间,有效降低升力扰动振荡频率;柔性翼型显著抑制了尾流流场的扰动,降低升力扰动振荡幅值,合适的弹性模量翼型使得扰动振荡完全消除。研究结果可为软飞行器气动设计提供参考。
Abstract:Compared with fixed wings, the flapping wing has a significant aerodynamic performance advantage at low speeds and low Reynolds numbers, which draws more and more attentions. But most previous studies focus on rigid flapping airfoils, the aerodynamic performances of flexible flapping airfoils are still unclear. A fluid-solid coupling model for the flexible elliptical airfoils was developed to analyze the flow field around the airfoil, the airfoil deformation and the aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils, at different wind speeds and attack angles. Compared with the rigid airfoil, the flexible airfoil can delay the shedding time of the wake vortex and reduce the oscillation frequency of the disturbance on the lift force. The flexible airfoil significantly suppresses the disturbance of the wake flow and reduces the oscillation amplitude of disturbance. Even, the airfoil disturbance oscillation can be completely eliminated at an appropriate Young’s modulus of the airfoil. These results provide a theoretical guidance for the design of soft aircraft.
-
Key words:
- flexible airfoil /
- fluid-solid coupling /
- aerodynamic performance /
- lift force /
- finite element
-
-
[1] 孙茂, 吴江浩. 昆虫飞行的高升力机理和能耗[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2003, 29(11): 970-977. (SUN Mao, WU Jianghao. Unsteady lift mechanisms and energetic in flying insects[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2003, 29(11): 970-977.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2003.11.004 [2] ELLINGTON C P, BERG C V D, WILLMOTT A P, et al. Leading-edge vortices in insect flight[J]. Nature, 1996, 384(6610): 626-630. doi: 10.1038/384626a0 [3] DICKINSON M H, LEHMANN F O, SANE S P. Wing rotation and the aerodynamic basis of insect flight[J]. Science, 1999, 284(5422): 1954-1960. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5422.1954 [4] TANG J, VIIERU D, SHYY W. A study of aerodynamics of low Reynolds number flexible airfoils[C]//37th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit. Miami, USA, 2007. [5] VISBAL M R, GORDNIER R E, GALBRAITH M C. High-fidelity simulations of moving and flexible airfoils at low Reynolds numbers[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2009, 46(5): 903-922. doi: 10.1007/s00348-009-0635-4 [6] 张兴伟, 周超英, 谢鹏. 扑翼柔性变形对悬停气动特性影响的数值研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2012, 44(1): 115-119.ZHANG Xingwei, ZHOU Chaoying, XIE Peng. Numerical study on the effect of flapping wing deformation on aerodynamic performance in hovering flight[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2012, 44(1): 115-119. (in Chinese) [7] 王姝歆, 周建华, 颜景平. 微小型仿生飞行机器人柔性翅的仿生设计与实验研究[J]. 实验流体力学, 2006, 20(1): 75-79. (WANG Shuxin, ZHOU Jianhua, YAN Jingping. Bionic design and experiment on flexible wings of a bionic flying micro-robot[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 20(1): 75-79.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9897.2006.01.018 [8] KANG W, ZHANG J Z, LEI P F, et al. Computation of unsteady viscous flow around a locally flexible airfoil at low Reynolds number[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2014, 46: 42-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.12.010 [9] 陶真新, 李绍斌, 宋西镇. 低雷诺数下柔性翼型气动性能分析[J]. 力学与实践, 2017, 39(2): 145-151.TAO Zhenxin, LI Shaobin, SONG Xizhen. The aerodynamic performance of a flexible airfoil at low Reynolds number[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2017, 39(2): 145-151. (in Chinese) [10] PESAVENTO U, WANG Z J. Flapping wing flight can save aerodynamic power compared to steady flight[J]. Physical Review Letter, 2009, 103(11): 118102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.118102 [11] 杨金广, 吴虎. 双方程k-ω SST湍流模型的显式耦合求解及其在叶轮机械中的应用[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(1): 116-124. (YANG Jinguang, WU Hu. Explicit coupled solution of two-equation k-ω SST turbulence model and its application in turbomachinery flow simulation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 116-124.(in Chinese) [12] MENTER F R. Zonal two equation k-ω turbulence models for aerodynamic flows[C]//AIAA 23rd Fluid Dynamics, Plasmadynamics, and Leaders Conference. Orlando, USA, 1993. -





 下载:
下载:





 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号