GPU Parallelization Computation of High-Dimensional Multi-Phase Separation in Complex Domains Based on the Corrected FPM
-
摘要:
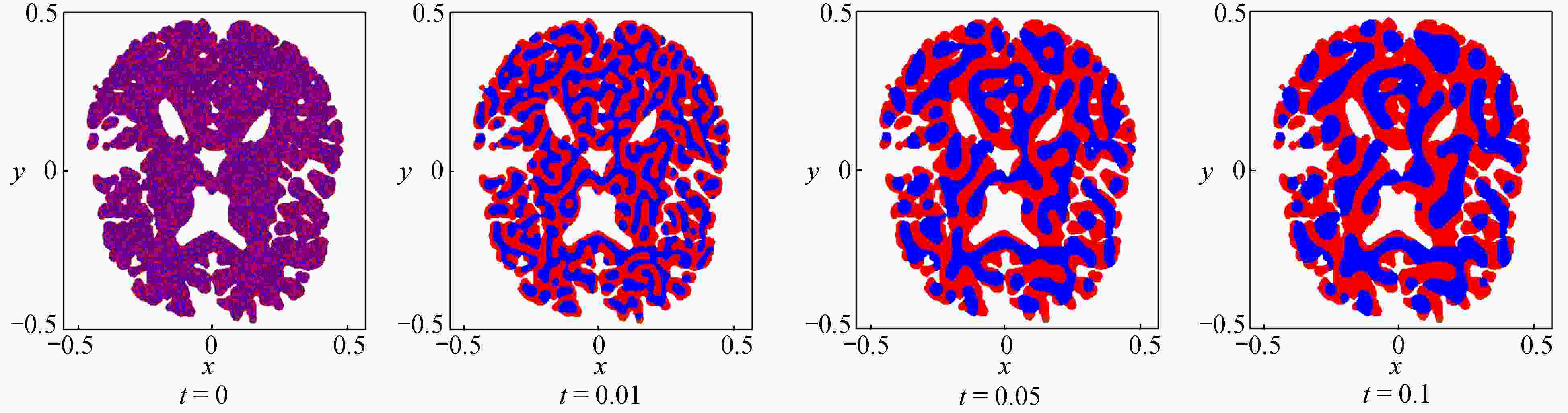
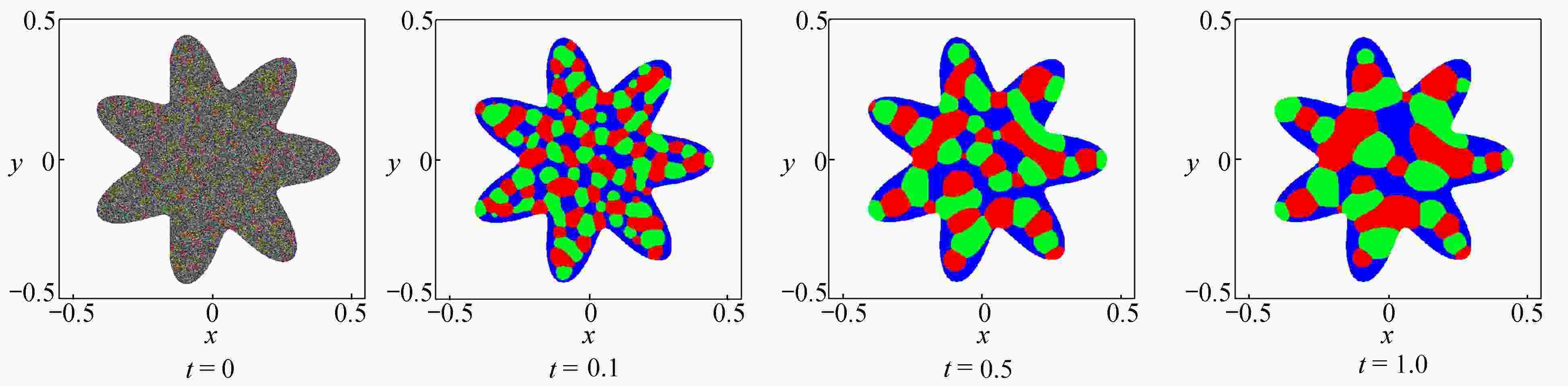
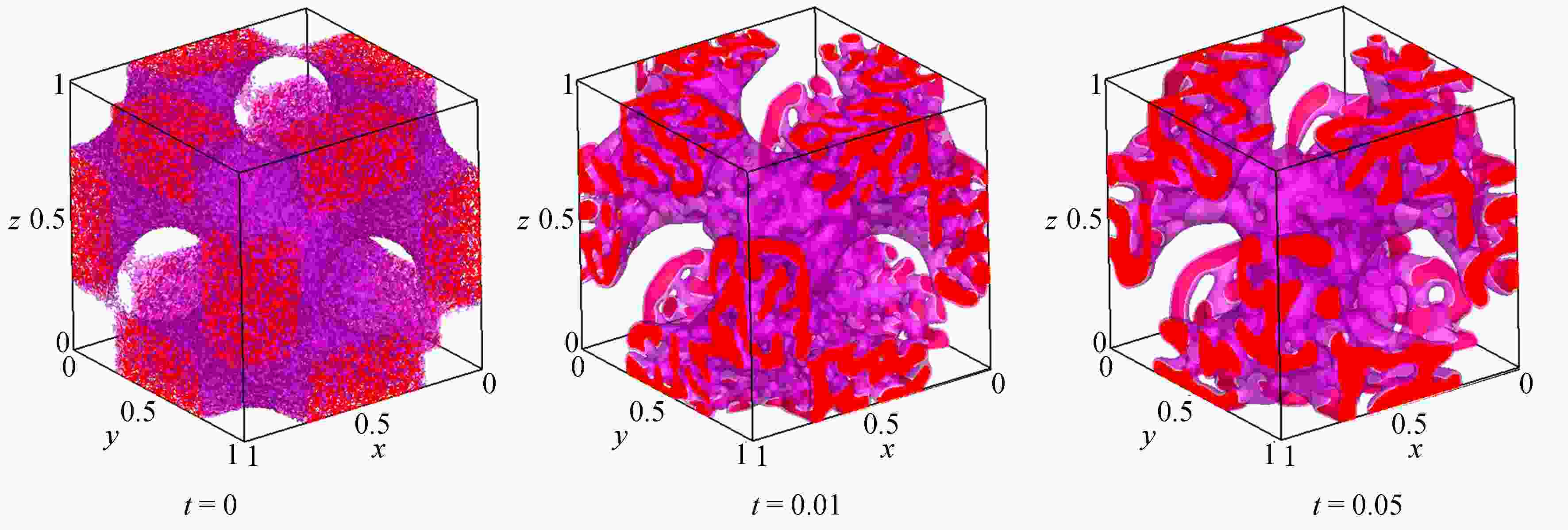
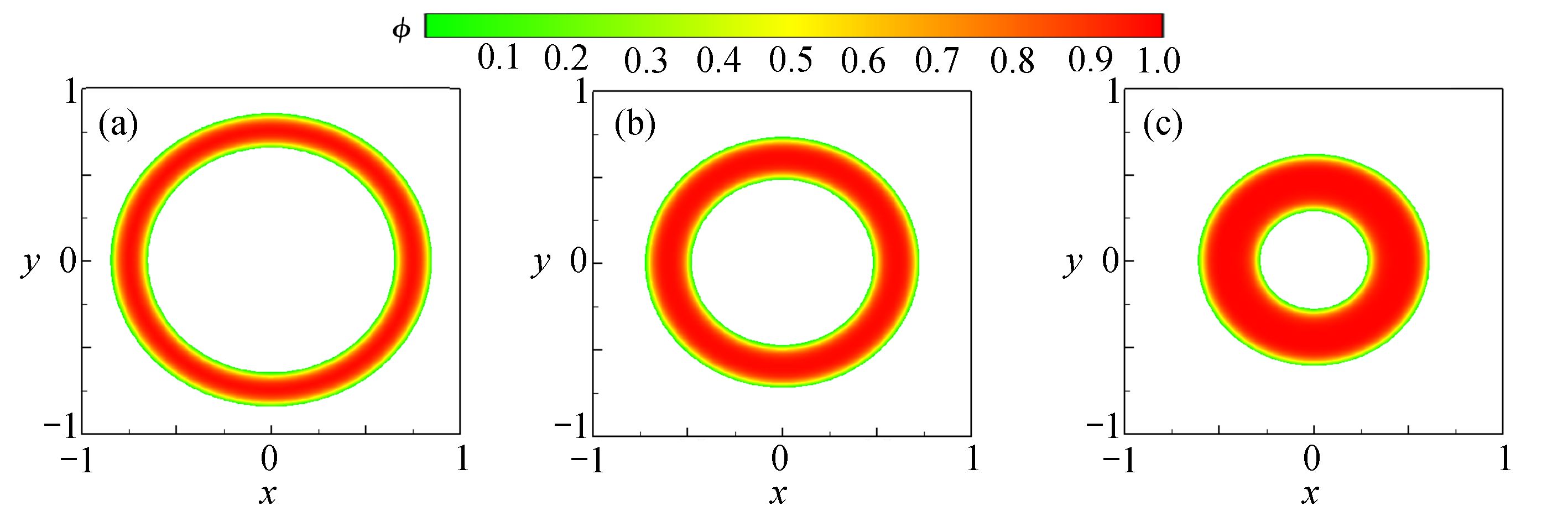
为了高效、准确地模拟高维多元Cahn-Hilliard (C-H)方程描述的复杂相分离过程,该文发展了一种基于纯无网格改进有限点集法(corrected finite pointset method, CFPM) 和CPU-GPU异构的快速并行算法 (简称为CFPM-GPU)。CFPM-GPU的构造过程为:① 基于Taylor展开和加权最小二乘思想,采用Wendland权函数推导出空间一/二阶导数的有限点集法(finite pointset method, FPM)格式;② 将多元C-H方程中四阶导数分为两个二阶导数,依次运用FPM对其离散得到C-H的改进FPM法(CFPM);③ 基于CUDA的单个GPU架构,首次给出了CFPM的一种并行算法以提高计算效率。 数值研究中,首先对二维径向或三维球对称C-H方程描述的相分离基准算例进行了求解,并与可靠结果作对比验证了提出的并行算法的准确性和高效性,单个CPU-GPU异构并行计算效率约是串行情况的160倍;其次,运用CFPM-GPU对复杂区域上二维/三维的两相或三相分离现象进行数值预测,并与其他方法结果做比较。数值结果表明,给出的CFPM-GPU能准确、高效地模拟二维/三维复杂区域上的多相分离过程。
-
关键词:
- FPM格式 /
- 三维多相分离 /
- 多元Cahn-Hilliard /
- GPU并行
Abstract:Based on the corrected finite pointset method (CFPM) with CPU-GPU heteroid parallelization (CFPM-GPU), a high-efficiency, accurate and fast parallel algorithm was developed for the high-dimensional phase separation phenomena governed by the multi-component Cahn-Hilliard (C-H) equation in complex domains. The proposed parallel algorithm with the CFPM-GPU was built in a process like: ① introduce the Wendland weight function into the discretization of the finite pointset method (FPM) scheme for the 1st/2nd spatial derivatives, based on the Taylor series and the weighted least square concept; ② use the above FPM scheme twice to approximate the 4th spatial derivative in the C-H equation, which is called the CFPM method; ③ for the first time establish an accelerating parallel algorithm for the CFPM with local matrices by means of a single GPU card based on the CUDA programming. Two benchmark problems of 2D radially and 3D spherically symmetric C-H equations were first solved to test the accuracy and high-efficiency of the proposed CFPM-GPU, and the acceleration ratio of the GPU parallelization to the single CPU computation is about 160. Subsequently, the proposed CFPM-GPU was used to predict the 2D/3D multi-phase separation phenomena in complex domains, and the prediction was compared with other numerical results. The numerical results show that, the proposed CFPM-GPU is valid and high-efficiency to simulate the 2D/3D multi-phase separation cases in complex domains.
-
表 1 不同节点数下,相邻节点标定消耗计算时间对比
Table 1. The consumed computing time for the calibration of neighbor nodes under different node numbers
node number computing time CPU TCPU/s GPU TGPU/s δSur $65 \times 65 \times 65$ 833.55 4.73 176.2 $129 \times 129 \times 129$ 51513.65 287.69 179.1 $257 \times 257 \times 257$ 3226951.32 17907.61 180.2 表 2 不同节点数下,每个时间层里物理量更新循环所需平均计算时间对比
Table 2. The average computing time costs at each time step under different node numbers
node number computing time CPU TCPU/s GPU TGPU/s δSur $65 \times 65 \times 65$ 10.332 0.065 158.95 $129 \times 129 \times 129$ 86.311 0.539 160.13 $257 \times 257 \times 257$ 725.281 4.525 160.28 -
[1] CHOKSI R, PELETIER M, WILLIAMS J F. On the phase diagram for microphase separation of diblock copolymers: an approach via a nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard functional[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2009, 69(6): 1712-1738. doi: 10.1137/080728809 [2] LI Y B, KIM J. Multiphase image segmentation using a phase-field model[J]. Computers and Mathematics With Applications, 2011, 62(2): 737-745. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2011.05.054 [3] 汪精英, 翟术英. 分数阶Cahn-Hilliard方程的高效数值算法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(8): 832-840WANG Jingying, ZHAI Shuying. An efficient numerical algorithm for fractional Cahn-Hilliard equations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(8): 832-840.(in Chinese) [4] CHARLES M E, HARALD G. Diffusional phase transitions in multicomponent systems with a concentration dependent mobility matrix[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1997, 109(3/4): 242-256. [5] DIEGEL A, FENG X B, WISE S M. Analysis of a mixed finite element method for a Cahn-Hilliard-Darcy-Stokes system[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2015, 53: 127-152. doi: 10.1137/130950628 [6] GUO Z, LIN P, LOWENGRUB J, et al. Mass conservative and energy stable finite difference methods for the quasi-incompressible Navier-Stokes-Cahn-Hilliard system: primitive variable and projection type schemes[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 326: 144-174. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2017.08.011 [7] ZHANG Z G, QIAO Z H. An adaptive time-stepping strategy for the Cahn-Hilliard equation[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2012, 11(4): 1261-1278. doi: 10.4208/cicp.300810.140411s [8] JEONG D, CHOI Y, KIM J. A benchmark problem for the two- and three-dimensional Cahn-Hilliard equation[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2018, 61: 149-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2018.02.006 [9] KIM J. A numerical method for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with a variable mobility[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2007, 12: 1560-1571. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2006.02.010 [10] JEONG D, YANG J X, KIM J. A practical and efficient numerical method for the Cahn-Hilliard equation in complex domains[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2019, 73: 217-228. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2019.02.009 [11] CHENG R J, CHENG Y M. Solving unsteady Schrödinger equation using the improved element-free Galerkin method[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2016, 25: 020203. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/2/020203 [12] DEHGHAN M, ABBASZADEH M. The meshless local collocation method for solving multi-dimensional Cahn-Hilliard, Swift-Hohenberg and phase field crystal equations[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2017, 78: 49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2017.02.005 [13] 王红, 李小林. 二维瞬态热传导问题的无单元Galerkin法分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(5): 460-469WANG Hong, LI Xiaolin. Analysis of 2D transient heat conduction problems with the element-free Galerkin method[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(5): 460-469.(in Chinese) [14] 曹维鸿, 傅卓佳, 汤卓超. 水槽动力特性数值模拟的新型局部无网格配点法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(4): 392-400CAO Weihong, FU Zhuojia, TANG Zhuochao. A novel localized meshless collocation method for numerical simulation of flume dynamic characteristics[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(4): 392-400.(in Chinese) [15] LIU G R, LIU M B, LI S. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: a mesh-free particle method[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2003, 33: 491. [16] 林晨森, 陈硕, 李启良, 等. 耗散粒子动力学GPU并行计算研究[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(10): 104702 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.104702LIN Chensen, CHEN Shuo, LI Qiliang, et al. Accelerating dissipative particle dynamics with graphic processing unit[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(10): 104702.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.63.104702 [17] JIANG T, CHEN Z C, LU W G, et al. An efficient split-step and implicit pure mesh-free method for the 2D/3D nonlinear Gross-Pitaevskii equations[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 231: 19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.05.007 [18] CRESPO A J C, DOMÍNGUEZ J M, ROGERS B D, et al. DualSPHysics: open-source parallel CFD solver based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics(SPH)[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2015, 187: 204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2014.10.004 [19] KING J R, POGORELOV I V, AMYX K M, et al. GPU acceleration and performance of the particle-beam-dynamics code Elegant[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2019, 235: 346-355. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.09.022 [20] HE F, ZHANG H S, HUANG C, et al. A stable SPH model with large CFL numbers for multi-phase flows with large density ratios[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 453: 110944. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.110944 [21] 杨秀峰, 刘谋斌. 瑞利-泰勒不稳定问题的光滑粒子法模拟研究[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(16): 164071YANG Xiufeng, LIU Moubin. Numerical study of Rayleigh-Taylor instability by using smoothed particle hydrodynamics[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(16): 164071.(in Chinese) [22] HE F, ZHANG H S, HUANG C, et al. Numerical investigation of the solitary wave breaking over a slope by using the finite particle method[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2020, 156: 103617. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2019.103617 [23] DANIEL W, MASSOUD R, WOLFGANG R. Neighbour lists for smoothed particle hydrodynamics on GPUs[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 225: 140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2017.12.014 [24] 任金莲, 蒋戎戎, 陆伟刚, 等. 基于局部加密纯无网格法非线性Cahn-Hilliard方程的模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2020, 69(8): 080202 doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20191829REN Jinlian, JIANG Rongrong, LU Weigang, et al. Simulation of nonlinear Cahn-Hilliard equation based on local refinement pure meshless method[J]. Acta Physics Sinica, 2020, 69(8): 080202.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20191829 [25] SUCHDE P, KUHNERT J, TIWARI S. On meshfree GFDM solvers for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2018, 165: 1-12. [26] SUDARSHAN T, JÖRG K. Modeling of two-phase flows with surface tension by finite pointset method (FPM)[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2007, 203: 376-386. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2006.04.048 [27] EDGAR O R F, IRMA D G C. Application of the finite pointset method to non-stationary heat conduction problems[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 71: 720-723. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.12.077 [28] LI Y B, CHOI J I, KIM J. Multi-component Cahn-Hilliard system with different boundary conditions in complex domains[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 323: 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2016.07.017 -




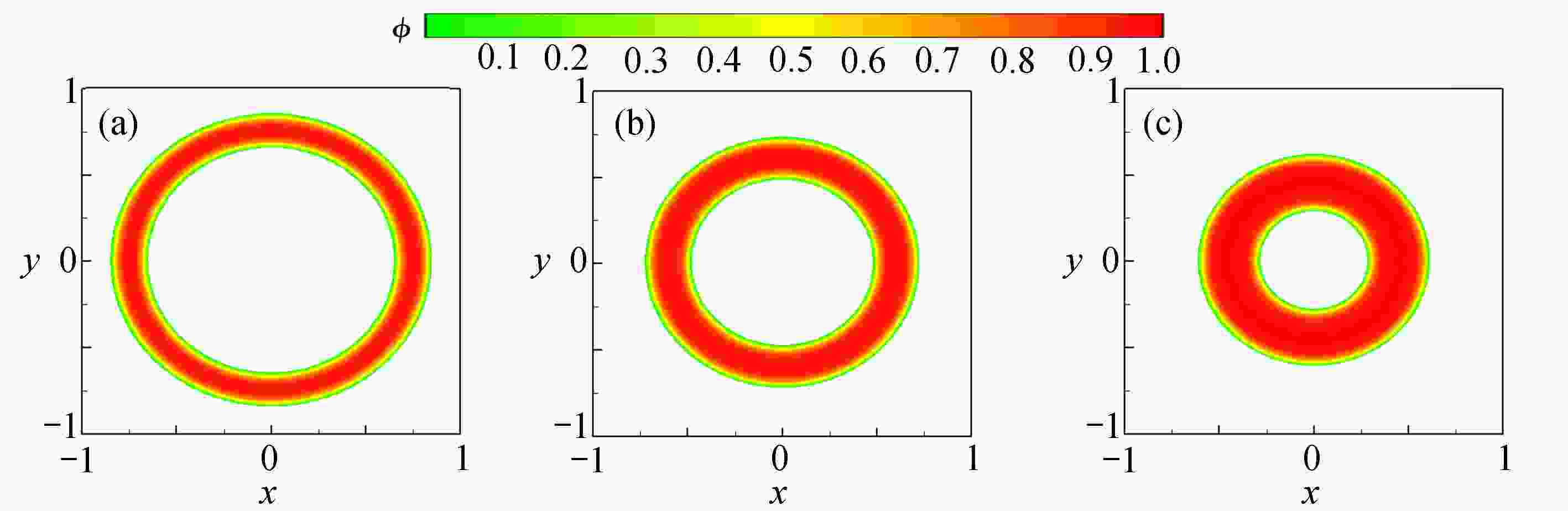
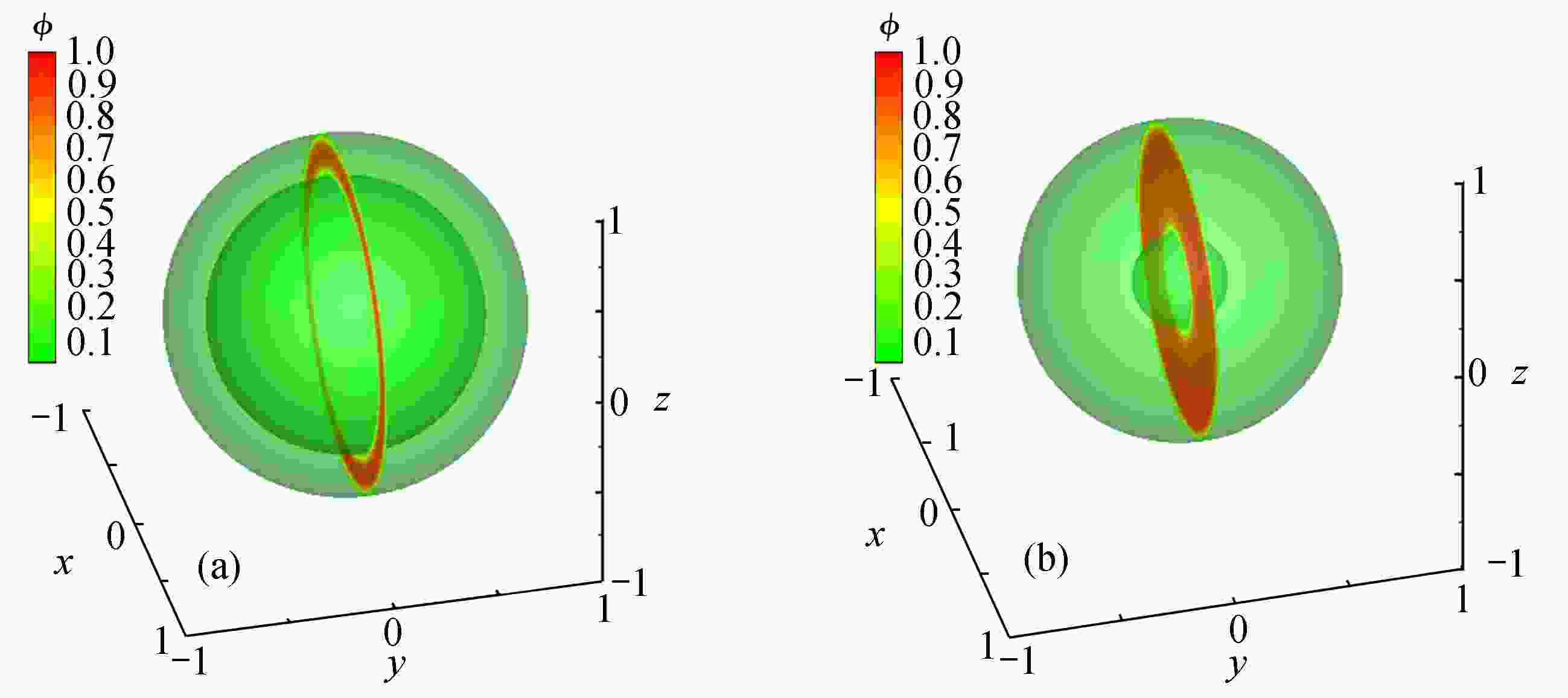
 下载:
下载:
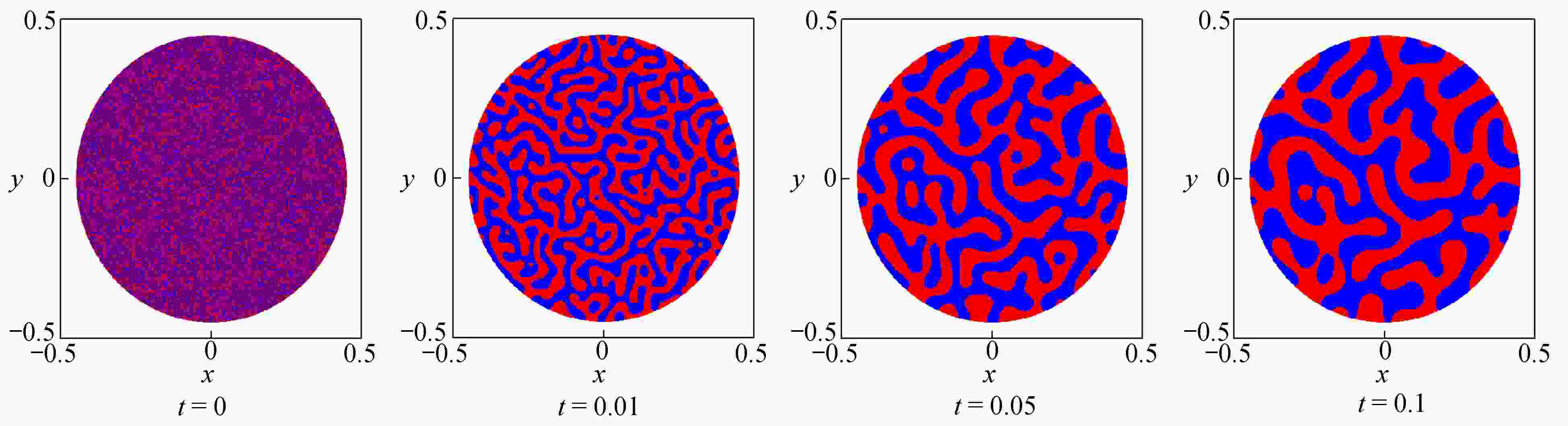
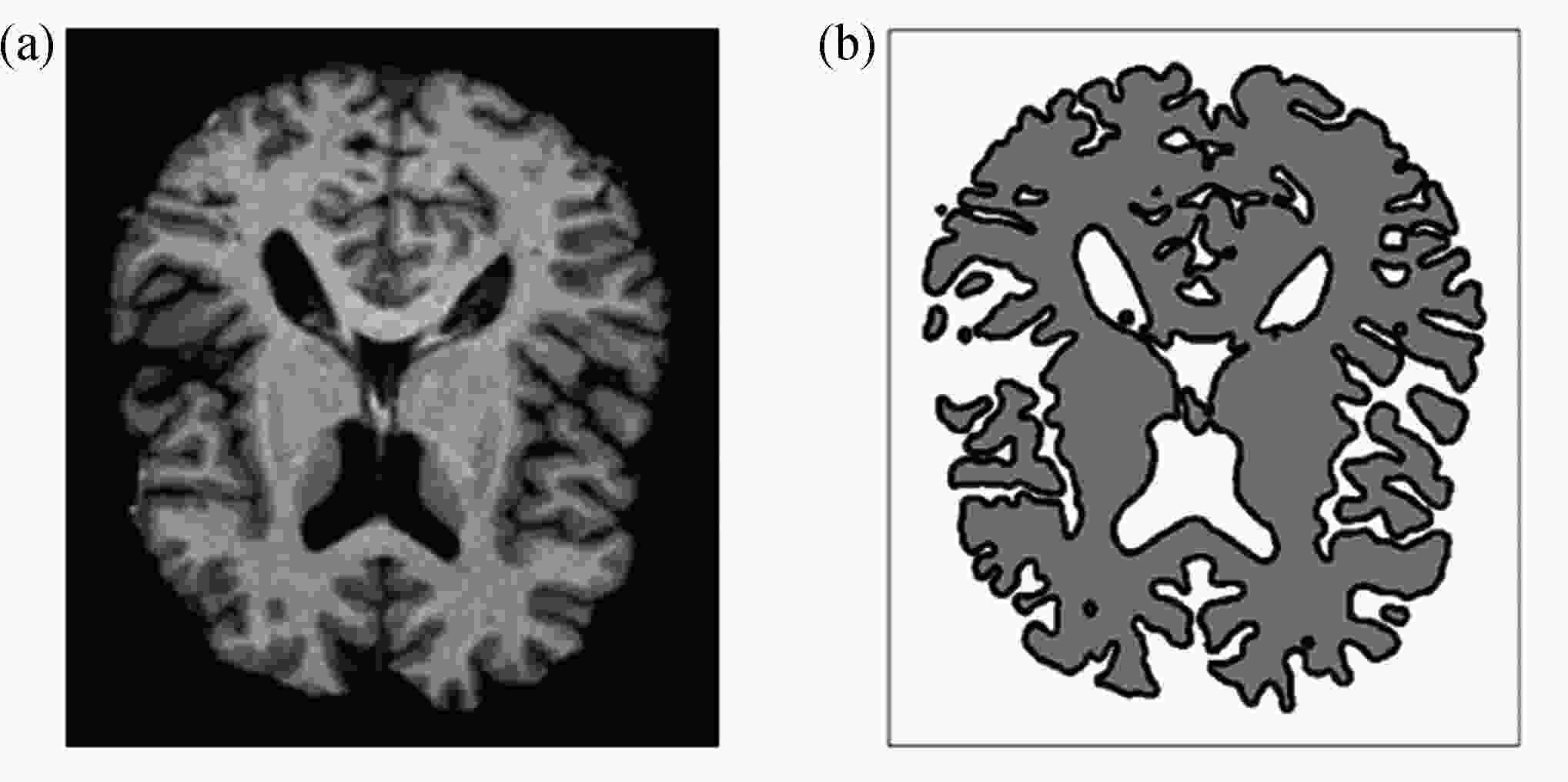


 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号